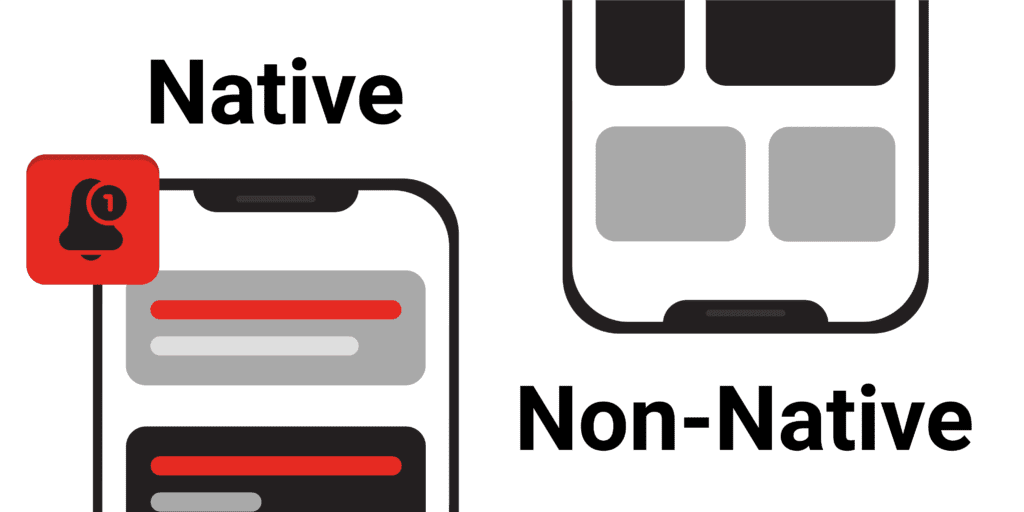
“Should we build Native Apps, Non-Native Apps, or Hybrid Apps for iOS and Android?”
We get this question all of the time. In most cases, the answer is yes, your mobile should be written in a native language.
The only times that you should consider building a non-native app or hybrid app are:
- if your end-user for the mobile app will not appreciate the benefits that the native app provides.
- Your nasty employer wants to make life difficult for your colleagues by having them enter a web form through a mobile app wrapper. 🙂
- You don’t have the resources to build native iOS and Android Apps.
What is a native mobile application?
A native application is a software program developed for use on a specific device or platform. The two main mobile operating systems are Apple’s iOS and Google’s Android. Apple’s iOS has two native languages: Swift and Objective-C. Mobile apps written in Swift and Objective-C will not run on an Android device, but these mobile apps will have the ability to use device-specific hardware, e.g. camera, GPS, and push notification systems .
A native app is installed directly onto your smartphone via the iOS App Store or Google Play. They require some sort of internet connectivity to download. In most cases, native apps don’t need the internet while using the application, unless you’re using platforms that require real-time information or interaction like online gaming or social media applications.
Native apps work with the device’s operating system in a way that enables them to work faster and deliver a mobile application, which is similar to the mobile apps that are pre-installed on your phones.
What is a non-native application?
Non-native or web applications offer many of the same features as native apps, but are not implemented as such. Web applications perform tasks by utilizing web browsers, including Safari, Chrome, and more. These applications are generally written in a browser-friendly language such as JavaScript, CSS, and HTML for universal use across multiple browsers.
What is a hybrid application?
Hybrid applications are a combination of native and non-native apps. They are built with the same mechanisms as non-native apps, e.g. JavaScript, CSS, and HTML, but they are installed from the iOS App Store and Google Play. Hybrid apps have access to the camera, GPS, and push notification system by going through generic wrappers that are customized to interface with the device’s hardware.
We have written Hybrid applications in React Native, Dart, and Xamarin.
React - We have inherited a number of React Native apps that are disasters. Typically, the developers will choose to focus on one platform, e.g. iOS. They will stop testing on Android. They’ll upgrade React a few times, and then come back and try to run Android. The Android will fail to run, and it will be challenging to get the Android to run.
Flow - We’ve had good luck with Flow for mobile applications that don’t require device hardware. Both Let’s Play Soccer and Puck Recruiter are written in Flow.
Xamarin - Xamarin was recently deprecated by Microsoft. Microsoft’s new push is with .NET MAUI. This significantly impacted one of our clients.
Top 7 reasons to build native apps
Our top 7 reasons to build a native mobile app vs. a non-native mobile app are:
1. Usability - By design, non-native mobile apps will have a completely different look and feel than native. On Android, few html5javascript solutions support Material Design. If you want the latest native experience, go for native software development.
2. If you’re building an enhanced version of an already existing app, e.g. Calendar, then people will expect your app to be as good as the Calendar app on iOS or Android. Building a non-native app that convincingly emulates a native app is a big challenge.
3. iOS and Android Upgrades – Html5javascript solutions are dependent upon PhoneGapCordova plugins for the non-native mobile app to reside in the App Store and Google Play. Open-source developers typically maintain these plugins. When new versions of iOS and Android are released, your app becomes dependent upon these developers to upgrade their plugins in order for your non-native mobile app to continue to work.
4. Suppose your app is heavily dependent upon integration with native resources, e.g. Calendar, Bluetooth, Camera, etc. In that case, the integration code will have to be written in native code by either you or a third party plugin.
5. Performance – Even when you tune up your non-native app, the non-native app will be noticeably slower on non-native frameworks.
6. Offline mode – If you do not have WiFi or 4G connectivity, your non-native app may not work because it’s not connected to the cloud. If you’ve written your app natively, then you can introduce a persistent data store, e.g. SQLite, that can store the data, and attempt to push the data once connectivity is reestablished.
7. At the end of the day, you want your users to be pleased with your app. If your app performs well, has the right look and feel, and is stable when the operating system upgrades, you have a solid foundation that ups the chances of your app’s success. When mobile app users encounter problems with a non-native mobile app, more often than not, they delete the app and never look back.
See how we can help
Related Articles
Top Software as a Service Companies in 2024
Spending for public cloud usage continues to climb with every year. In 2023, nearly $600 billion was spent world-wide with a third of that being taken up by SaaS. By comparison, Infrastructure as a Service only takes up $150 billion and Platform as a Service makes up $139 billion. On average, companies use roughly 315 individual SaaS applications for their operations and are gradually increasing on a yearly basis. SaaS offers a level of cost efficiency that makes it an appealing option for consuming software.
AWS Graviton and Arm-architecture Processors
AWS launched its new batch of Arm-based processors in 2018 with AWS Graviton. It is a series of server processors designed for Amazon EC2 virtual machines. The EC2 AI instances support web servers, caching fleets, distributed data centers, and containerized microservices. Arm architecture is gradually being rolled out to handle enterprise-grade utilities at scale. Graviton instances are popular for handling intense workloads in the cloud.
What is Tiered Pricing for Software as a Service?
Tiered Pricing is a method used by many companies with subscription models. SaaS companies typically offer tiered pricing plans with different services and benefits at each price point with typically increasing benefits the more a customer pays. Striking a balance between what good rates are and the price can be difficult at times.


Joel Garcia has been building AllCode since 2015. He’s an innovative, hands-on executive with a proven record of designing, developing, and operating Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), mobile, and desktop solutions. Joel has expertise in HealthTech, VoIP, and cloud-based solutions. Joel has experience scaling multiple start-ups for successful exits to IMS Health and Golden Gate Capital, as well as working at mature, industry-leading software companies. He’s held executive engineering positions in San Francisco at TidalWave, LittleCast, Self Health Network, LiveVox acquired by Golden Gate Capital, and Med-Vantage acquired by IMS Health.